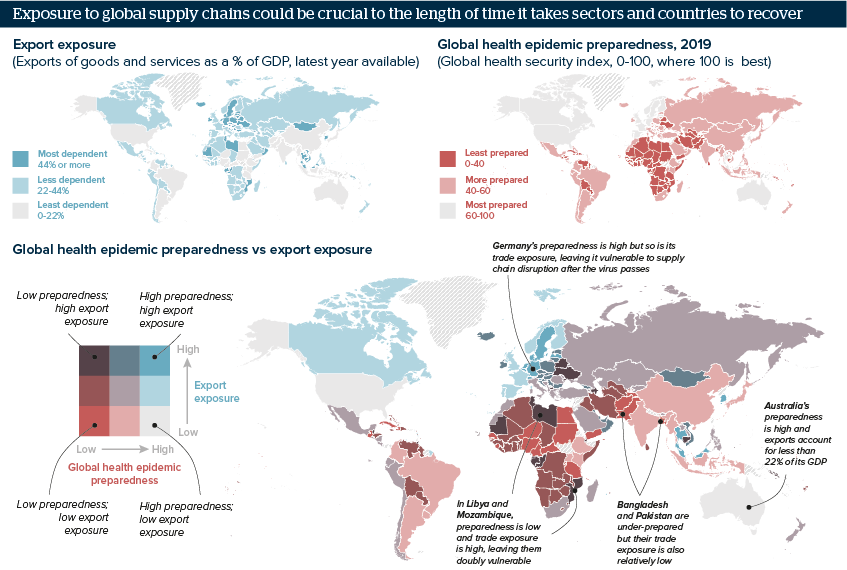
Health preparedness and trade affect COVID-19 exposure
Although health systems are crucial in mitigating the impact of the COVID-19 outbreak, trade exposure is also key
Source: Global Health Security Index, October 2019, World Bank World Development Indicators
Outlook
There are 80,152 cases of the COVID-19 outbreak in China and more than 12,000 elsewhere. Travel restrictions, business shutdowns and quarantines are mounting.
In October 2019, experts constructed a global health security index for 195 countries to assess how prepared countries are for an infectious disease outbreak. Italy and Iran, two countries that have suffered more than 50 deaths from the virus, scored relatively low on the index, as did Japan, one of the first countries that the virus spread to.
Supply chains will be slower than many domestic sectors to recover because they are more likely to encounter bottlenecks as different countries remove travel and business restrictions at different rates. Countries reliant on trade, including South Korea and Germany, will be vulnerable to disruption long after the virus passes.
Impacts
- COVID-19 is a supply shock; stimulus will cushion business activity but spending and rate cuts will be slow to aid complex supply chains.
- Global cooperation in areas such as data sharing will be key to preparations, but fear and weak GDP growth may prompt more nationalism.
- In China, fiscal and monetary stimulus will mitigate the impact of the virus on growth and jobs, reducing the risk of political unrest.
See also
- Manufacturers will seek diversification and resilience - May 21, 2020
- Mining supply disruptions mask mounting demand fears - May 5, 2020
- Pandemic triggers European rethink on supply chains - May 4, 2020
- COVID-19 poses a huge challenge to developing nations - Apr 8, 2020
- Vulnerable developing states face an L-shaped recovery - Mar 31, 2020
- Markets fear inadequacy of monetary and fiscal moves - Mar 30, 2020
- COVID-19 global climate impact may be brief - Mar 27, 2020
- COVID-19 will hit US GDP but recovery may be V-shaped - Mar 16, 2020
- COVID-19 will worsen the global manufacturing downturn - Mar 13, 2020
- Latin American containment measures spread with virus - Mar 12, 2020
- Italy will struggle to emerge from recession this year - Mar 10, 2020
- COVID-19 impact will be worse than flu - Mar 9, 2020
- India will come under heavy strain over COVID-19 - Mar 5, 2020
- COVID-19 will challenge Latin American health systems - Mar 5, 2020
- Dollar strength will add to US exporters’ woes - Mar 4, 2020
- Near-term financial market virus fears will be strong - Mar 2, 2020
- Coronavirus may cut global growth to 2% in early 2020 - Feb 10, 2020
- More graphic analysis